Table of Contents
People with Parkinson’s Disease often develop mental symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions. These may be caused by the disease or the drugs used to treat it.
Most people with PD have rhythmic shaking, called tremors. They also have slow movement, called bradykinesia, and muscle stiffness or rigidity.
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disorder is due to nerve mobile dying or degeneration within the basal ganglia, the mind area answerable for controlling motion. These cells make dopamine, a chemical that carries messages to help your frame flow easily and flippantly. When the cells begin to die, dopamine stages drop and your body would not ship as many messages approximately motion. That’s when you begin to be aware of signs like trembling or shaking, and you can additionally have problems walking, balance, and stiffness.
There’s no recognized manner to save you from Parkinson’s ailment, however, some matters can increase your risk. These encompass having a family history of the disease, publicity of certain pollution to your environment, head trauma, or despair. Specific genes also can make you much more likely to get Parkinson’s.
Once you are diagnosed with Parkinson’s, you can begin to manage your symptoms with medication. Many different drugs can reduce tremors, stiffness, and sluggish motions. Your doctor will recommend a medication depending on your particular symptoms and requirements. You can better control your medication while understanding Parkinson’s disease with regular visits to your neurologist, who has experience treating patients with PD. They’ll help you adjust your doses as your condition progresses and your tolerance changes. It can help you have the best possible quality of life with Parkinson’s disease.

Symptoms
The 4 primary signs of Parkinson’s disease (PD) are tremors, muscle stiffness, sluggish movement (bradykinesia), and balance and coordination troubles. These symptoms arise whilst nerve cells that produce dopamine inside the mind die or end up impaired. PD symptoms typically begin in just one hand or leg and progress progressively through the years.
A tremor, an intricate rhythmic quiver, commences within a solitary part of your corporeal form, often manifesting in the hand or digits. As the malady of Parkinson’s advances, it may disseminate to the contralateral hand or lower extremity, the axial core of your physique, or even your visage and mandible. The tremulous manifestations become more conspicuous during periods of repose or quiescence. Concurrently, you might also perceive a dearth of countenance animation, diminished ocular flutter, or subdued and languorous utterance, along with minuscule penmanship, which is medically termed micrographia.
Additional indicators of Parkinson’s disease encompass an attenuated carriage, obstacles revolving within the confines of your sleeping berth, and somnolent tribulations. Concurrently, psychological perturbations in the form of despondency or anxiety may manifest. A depreciation in the acuity of olfactory perception, identified as hyposmia, or an incapacity to discern gustatory stimuli, denominated anosmia, is likewise a recurrent occurrence.
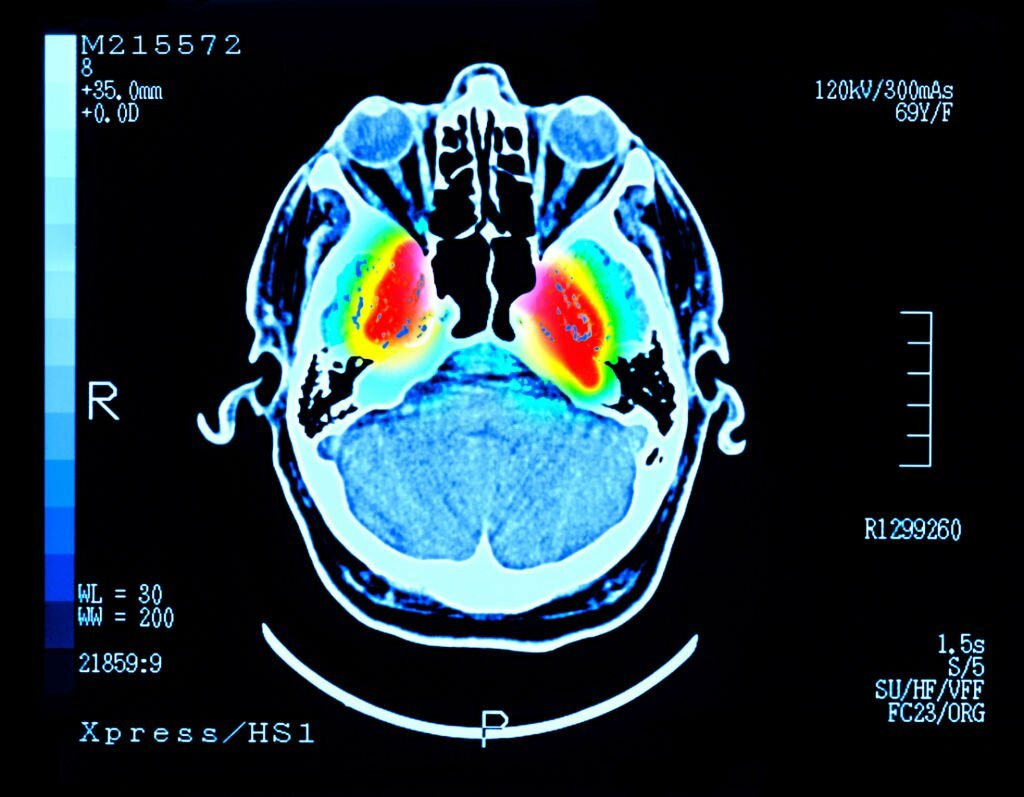
Your medical practitioner will meticulously evaluate your manifestations and medical historiography to delineate the presence of Parkinson’s disease. They may subject you to cranial tomography or magnetic resonance imaging to gain insight into your corporeal interior. These diagnostic modalities facilitate the identification of compromised encephalic tissue and zones of pathology. Furthermore, they possess the capability to unveil the presence of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease. Other diagnostic examinations that may be contemplated encompass cutaneous biopsy and lumbar puncture. The latter entails the introduction of a cannula into the vertebral canal to withdraw cerebrospinal fluid for analytical scrutiny.
Diagnosis
The inaugural step in the diagnostic expedition for Parkinson’s disease encompasses a comprehensive medical chronicle and corporeal inspection, which incorporates inquiries about genealogical antecedents and contemporary pharmacotherapy, inclusive of micronutrient supplements. A few medications have the proclivity to elicit symptoms akin to those synonymous with Parkinson’s disease.
The quintessential clinical manifestation of Parkinson’s disease is the presence of tremors, the oscillatory agitation, most frequently localizing to one upper extremity, the thumb, or the index finger, classically recognized as the ‘pill-rolling’ tremor. As the ailment advances, these tremors may diffusely propagate to assorted anatomical regions, including the lower limbs, upper limbs, countenance, thoracic area, or the pharyngeal region. Furthermore, bradykinesia, characterized by languid motor activity, may ensue. Motor responses may transmute into a more rigid demeanor, thereby obfuscating supination or extension. Ambulation might become accompanied by a dragging or shuffling ambiance.
Ancillary indicators encompass postural instability, ambulatory dysfunction, myotonic rigidity, and a subdued vocal resonance. The populace afflicted by Parkinson’s disease frequently grapples with affective maladies such as anxiety and despondency. Additionally, somnolence may become problematic, and concomitant with a general sense of disquietude or cognitive disturbances, perturbations in attentiveness, and memory lapses.
Parkinson’s disease remains bereft of a solitary diagnostic modality. Your healthcare provider shall assess your clinical manifestations employing an evaluative scale, for instance, the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), coupled with an exploration of your medical chronicle. Thereafter, neurological scrutiny will be conducted, scrutinizing facets of agility, myotonic tension, and motility. Subsequently, your medical practitioner may proscribe the administration of carbidopa-levodopa (Rytary, Sinemet) to gauge its impact on symptomatology.
Treatment
Presently, available interventions hold the capacity to ameliorate symptoms; nonetheless, they do not impede the relentless progression of Parkinson’s disease. Surgical procedures may proffer respite to select individuals.
The effectiveness of therapeutic modalities is most pronounced when instituted expeditiously. Early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease fosters the timely commencement of pertinent interventions, thereby allowing accruing benefits. This ailment is occasioned by the attrition of encephalic neurons responsible for the synthesis of dopamine. This culminates in a disruption in the transmission of motor directives, subsequently giving rise to tremulous manifestations. The great post read about totally science GitLab.
Pharmacological agents are equipped to palliate symptomatology but fall short of a curative resolution, mandating uninterrupted administration. Levodopa (L-dopa) constitutes the cornerstone of pharmacotherapy for Parkinson’s disease. It is frequently co-administered with carbidopa, which serves to inhibit the peripheral enzymatic degradation of levodopa before its cerebral penetration, augmenting the magnitude of its therapeutic effect. The adjunctive carbidopa therapy concurrently mitigates the emergence of unwanted sequelae, such as involuntary motor movements.
Alternate pharmaceutical preparations target diverse symptomatology, encompassing tremors and rigidity. Anticholinergic agents, inclusive of ropinirole (Requip) and pramipexole (Mirapex), evince the ability to govern tremors and enhance myotonic governance. Certain pharmaceutical compounds stimulate the biosynthesis of dopamine in the encephalon. These include dopamine agonists such as apomorphine (Apokyn) and rotigotine (Neupro). Notably, particular complementary and alternative treatments (CAT) may intersect with select Parkinson’s pharmacotherapeutics; thus, a comprehensive discourse with your healthcare professional remains imperative.

Liam Stephens is a dynamic and skilled blogger, recognized for his ability to identify trends and create compelling content. As the founder of Remi-Portrait.com, Liam has become a reliable source of information across various fields such as food, technology, health, travel, business, lifestyle, and current events. He specializes in delivering up-to-date technology news and insights, catering to the diverse community that surrounds Remi-Portrait.com. His proficiency and engaging writing style have earned him a dedicated audience, solidifying his reputation in the digital sphere.