When it comes to skin growths, particularly in sensitive areas, distinguishing between skin tags and genital warts is crucial for appropriate management and treatment. This article aims to provide a detailed comparison of these two common skin conditions, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What are Skin Tags?
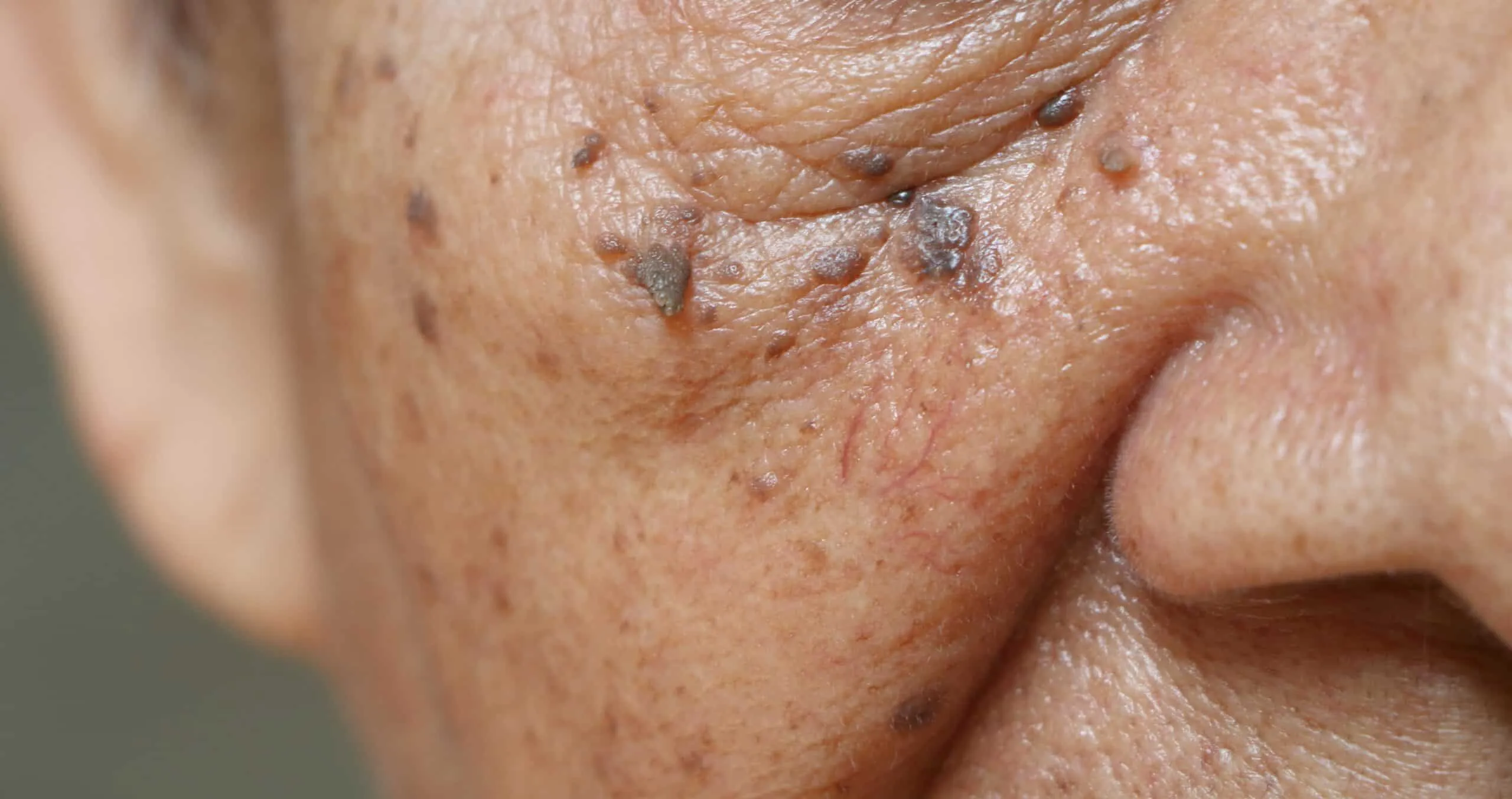
Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, are small, soft, flesh-colored benign skin growths. They typically develop in areas where skin rubs against skin or clothing, such as the neck, armpits, groin, and under the breasts. Skin tags are composed of loose collagen fibers and blood vessels surrounded by skin. Although they are harmless and non-cancerous, they can be a cosmetic concern or cause discomfort when snagged by clothing or jewelry.
What are Genital Warts?
Genital warts, on the other hand, are contagious growths that appear in the genital and anal areas. They are caused by certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly HPV types 6 and 11, which account for about 90% of cases. Genital warts are characterized by their flesh-colored or gray swellings in the genital area. They can grow as a single wart or in clusters resembling a cauliflower.
For those seeking a solution for genital warts, understanding your treatment options is essential. From topical creams to advanced surgical procedures, the right treatment can effectively manage and possibly eliminate genital warts. To explore comprehensive information and expert advice on finding a genital warts cure, visit our dedicated resource. This website offers insights into the latest treatments and preventive measures, ensuring you make informed decisions about your health.
Symptoms and Identification
The primary symptom of skin tags is the appearance of a flesh-colored growth on the skin that is soft and movable. They are typically painless and do not change over time. In contrast, genital warts may cause symptoms such as itching, discomfort, and bleeding with intercourse. Unlike skin tags, genital warts may feel slightly bumpy or rough to the touch.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for skin tags include obesity, diabetes, pregnancy, and genetics. They are also more common in adults and tend to increase in frequency with age. For genital warts, the primary risk factor is unprotected sexual contact with an infected partner. The virus can be transmitted even when an infected partner shows no signs of warts.
Treatment Options
Treatment for skin tags involves several options:
- Snipping: Using sterile scissors to remove the skin tag.
- Cryotherapy: Applying liquid nitrogen to freeze off the skin tag.
- Electrocauterization: Burning off the skin tag using electric current.
Treatment for genital warts includes:
- Topical Treatments: Prescription creams like imiquimod or podofilox that help reduce wart size.
- Cryotherapy: Similar to skin tags, but with careful consideration to avoid damage to surrounding sensitive skin.
- Surgical Removal: In severe cases, laser surgery or excision might be recommended.
Prevention
Preventing skin tags revolves primarily around reducing friction by maintaining a healthy weight and wearing loose clothing. To prevent genital warts, the use of condoms during intercourse is essential, although they do not provide 100% protection against HPV. Vaccination against HPV is also highly effective in preventing genital warts and other complications like cervical cancer.
When to See a Doctor
It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any new growths on your skin or genitals, to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This is especially important for genital warts, as HPV can have long-term health implications.
Final Thought
Both skin tags and genital warts are common conditions that can be effectively treated, but understanding the differences between them is key to management and prevention. If you have concerns about any skin growths, a healthcare provider can offer advice and treatment options tailored to your condition.