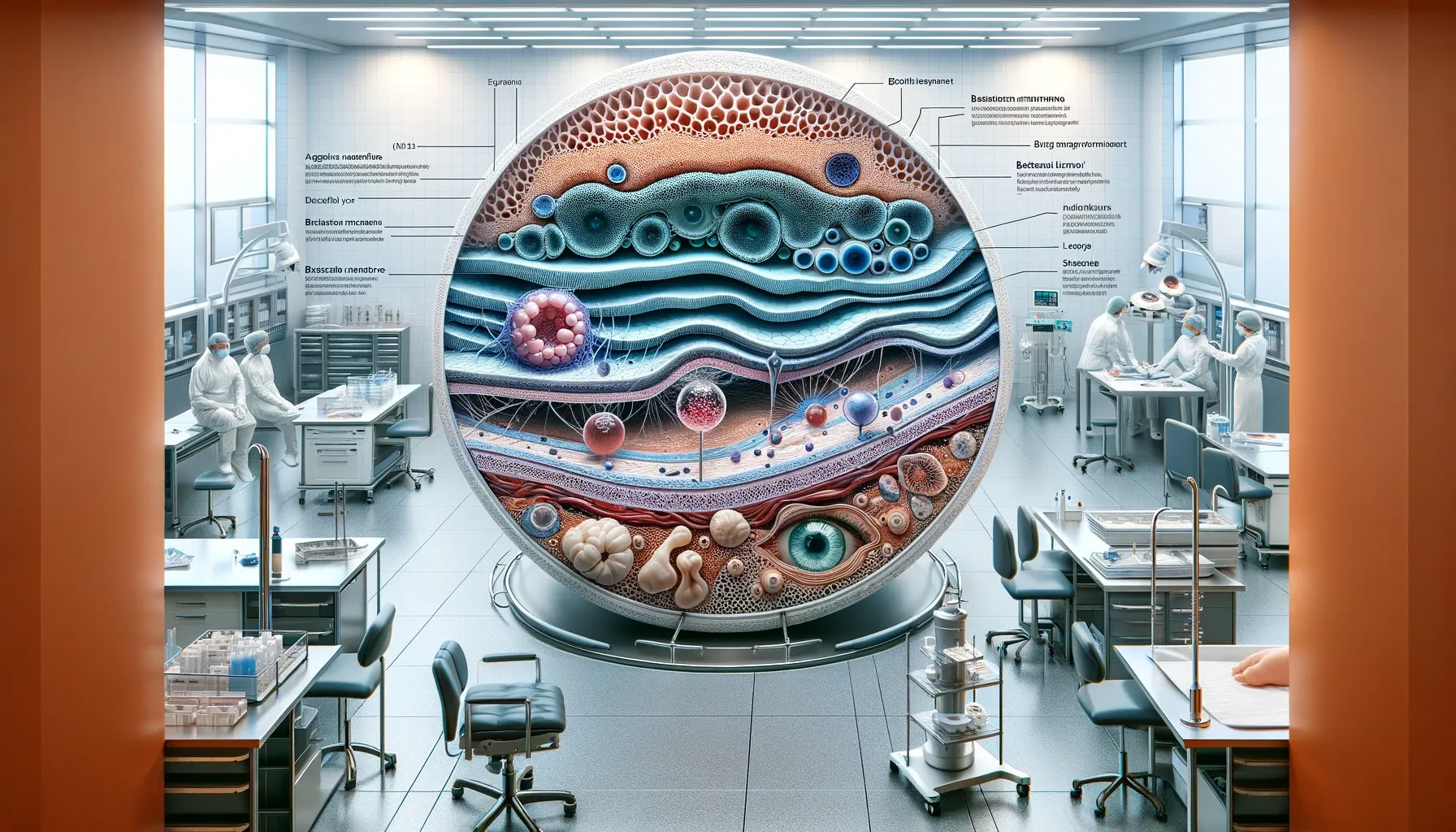
The amniotic membrane, an essential component of prenatal development, is gaining prominence in medical applications due to its unique healing properties. This article delves into what the membrane is, its composition, medical uses, and the future of its applications.
Understanding the Amniotic Membrane
The amniotic membrane is the innermost layer of the placenta, consisting of a thin but sturdy structure. It surrounds the fetus during pregnancy, providing a protective environment. Composed of a unique combination of cells, it has properties that are invaluable in regenerative medicine.
Composition of the Amniotic Membrane
- Epithelial Cells: Line the membrane, playing a role in reducing inflammation and scarring.
- Extracellular Matrix: Rich in collagen types, providing strength and elasticity.
- Growth Factors: Essential for tissue growth and wound healing.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Help in reducing inflammation in damaged tissues.
- Medical Uses of the Membrane
- Wound Healing: Used in chronic wounds, burns, and surgical sites.
- Ophthalmology: In corneal transplant surgery and other eye conditions.
- Orthopedics: To enhance tendon repair and reduce joint inflammation.
- Dental Surgery: In periodontal procedures and oral tissue regeneration.
The Healing Properties of the Amniotic Membrane
The membrane promotes healing through multiple mechanisms:
- Reducing Inflammation: Its anti-inflammatory properties help in managing wound inflammation.
- Preventing Scarring: Its epithelial composition minimizes fibrosis and scarring.
- Enhancing Tissue Regeneration: Growth factors aid in the regeneration of damaged tissues.
Harvesting and Processing of Amniotic Membranes
Amniotic membranes are harvested during cesarean sections, with donors’ consent. The membrane is then processed and sterilized for medical use, ensuring safety and preserving its biological properties.
Advantages Over Conventional Treatments
The membrane offers several benefits:
- Reduced Infection Risk: Natural antibacterial properties help in reducing the risk of infections.
- Biocompatibility: Minimizes the risk of rejection and adverse immune reactions.
- Versatility: Can be used in various forms, including grafts, sheets, or as a suspension.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
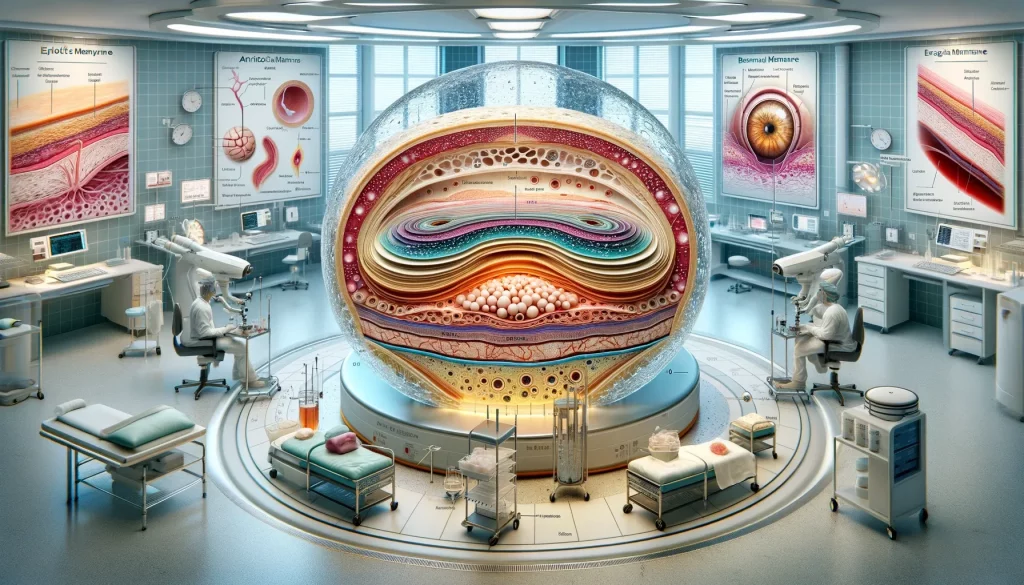

Safety protocols in harvesting, processing, and storage are critical. Ethical considerations involve informed consent from donors and adherence to medical and ethical guidelines in the use of human tissues.
Challenges and Limitations
While beneficial, there are challenges:
- Preservation and Storage: Requires specific conditions to maintain its properties.
- Cost and Availability: Can be expensive and not always readily available.
- Limited Research: More studies are needed to understand the full potential and limitations.
Recent Advancements in Amniotic Membrane Applications
Advancements include:
- Improved Preservation Techniques: Enhancing the longevity and efficacy of stored membranes.
- Combination Therapies: Using amniotics in conjunction with other regenerative techniques.
- Expanded Applications: Exploring new areas of use in medicine, including nerve repair and cosmetic surgery.
Preparing for a Procedure Using Amniotic Membrane
For patients undergoing treatment with amniotic membranes, understanding the procedure, potential risks, and recovery expectations is important.
Future Directions in Amniotic Membrane Research
Research is expanding into bioengineering, where membranes could be modified for specific medical applications, and exploring its potential in treating more complex conditions.
The amniotic membrane is a remarkable biological material with diverse applications in medicine. Its ability to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and minimize scarring makes it a valuable tool in regenerative medicine. As research advances, its applications are likely to expand, offering new solutions to complex medical challenges.